Examples¶
Beam structure¶
This example for a simple beam structure gives basic overview of the input file (found under tests/sm/beam2d_1.in). Structure geometry and its constitutive and geometrical properties are shown in Fig. (ex01). The linear static analysis is required, the influence of shear is neglected.
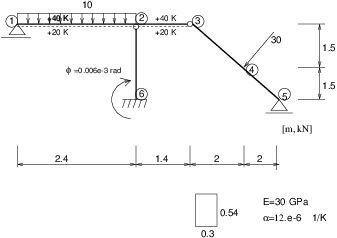
Example 1 - beam2d_1.in¶
beam2d_1.out
Simple Beam Structure - linear analysis
#only momentum influence to the displacements is taken into account
#beamShearCoeff is artificially enlarged.
StaticStructural nsteps 3 nmodules 0
domain 2dBeam
OutputManager tstep_all dofman_all element_all
ndofman 6 nelem 5 ncrosssect 1 nmat 1 nbc 6 nic 0 nltf 3 nset 7
node 1 coords 3 0. 0. 0.
node 2 coords 3 2.4 0. 0.
node 3 coords 3 3.8 0. 0.
node 4 coords 3 5.8 0. 1.5
node 5 coords 3 7.8 0. 3.0
node 6 coords 3 2.4 0. 3.0
Beam2d 1 nodes 2 1 2
Beam2d 2 nodes 2 2 3 DofsToCondense 1 6
Beam2d 3 nodes 2 3 4 DofsToCondense 1 3
Beam2d 4 nodes 2 4 5
Beam2d 5 nodes 2 6 2 DofsToCondense 1 6
SimpleCS 1 area 1.e8 Iy 0.0039366 beamShearCoeff 1.e18 thick 0.54 material 1 set 1
IsoLE 1 d 1. E 30.e6 n 0.2 tAlpha 1.2e-5
BoundaryCondition 1 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 1 3 values 1 0.0 set 4
BoundaryCondition 2 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 1 5 values 1 0.0 set 5
BoundaryCondition 3 loadTimeFunction 2 dofs 3 1 3 5 values 3 0.0 0.0 -0.006e-3 set 6
ConstantEdgeLoad 4 loadTimeFunction 1 Components 3 0.0 10.0 0.0 loadType 3 set 3
NodalLoad 5 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 3 1 3 5 Components 3 -18.0 24.0 0.0 set 2
StructTemperatureLoad 6 loadTimeFunction 3 Components 2 30.0 -20.0 set 7
PeakFunction 1 t 1.0 f(t) 1.
PeakFunction 2 t 2.0 f(t) 1.
PeakFunction 3 t 3.0 f(t) 1.
Set 1 elementranges {(1 5)}
Set 2 nodes 1 4
Set 3 elementedges 2 1 1
Set 4 nodes 2 1 5
Set 5 nodes 1 3
Set 6 nodes 1 6
Set 7 elements 2 1 2
Plane stress example¶
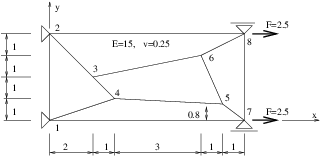
Example 2¶
patch100.out
Patch test of PlaneStress2d elements -> pure compression
LinearStatic nsteps 1
domain 2dPlaneStress
OutputManager tstep_all dofman_all element_all
ndofman 8 nelem 5 ncrosssect 1 nmat 1 nbc 3 nic 0 nltf 1 nset 3
node 1 coords 3 0.0 0.0 0.0
node 2 coords 3 0.0 4.0 0.0
node 3 coords 3 2.0 2.0 0.0
node 4 coords 3 3.0 1.0 0.0
node 5 coords 3 8.0 0.8 0.0
node 6 coords 3 7.0 3.0 0.0
node 7 coords 3 9.0 0.0 0.0
node 8 coords 3 9.0 4.0 0.0
PlaneStress2d 1 nodes 4 1 4 3 2 NIP 1
PlaneStress2d 2 nodes 4 1 7 5 4 NIP 1
PlaneStress2d 3 nodes 4 4 5 6 3 NIP 1
PlaneStress2d 4 nodes 4 3 6 8 2 NIP 1
PlaneStress2d 5 nodes 4 5 7 8 6 NIP 1
Set 1 elementranges {(1 5)}
Set 2 nodes 2 1 2
Set 3 nodes 2 7 8
SimpleCS 1 thick 1.0 width 1.0 material 1 set 1
IsoLE 1 d 0. E 15.0 n 0.25 talpha 1.0
BoundaryCondition 1 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 2 1 2 values 1 0.0 set 2
BoundaryCondition 2 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 1 2 values 1 0.0 set 3
NodalLoad 3 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 2 1 2 components 2 2.5 0.0 set 3
ConstantFunction 1 f(t) 1.0
Examples - parallel mode¶
Node-cut example¶
The example shows explicit direct integration analysis of simple structure with two DOFs. The geometry and partitioning is sketched in fig.(nodecut-ex01).
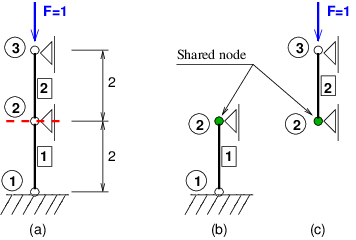
Node-cut partitioning example: (a) whole geometry, (b) partition 0, (c) partition 1.¶
#
# partition 0
#
partest.out.0
Parallel test of explicit oofem computation
#
NlDEIDynamic nsteps 3 dumpcoef 0.0 deltaT 1.0
domain 2dTruss
#
OutputManager tstep_all dofman_all element_all
ndofman 2 nelem 1 ncrosssect 1 nmat 1 nbc 3 nic 0 nltf 1 nset 4
#
Node 1 coords 3 0. 0. 0.
Node 2 coords 3 0. 0. 2. Shared partitions 1 1
Truss2d 1 nodes 2 1 2
Set 1 elements 1 1
Set 2 nodes 2 1 2
Set 3 nodes 1 1
Set 4 nodes 0
SimpleCS 1 thick 0.1 width 10.0 material 1 set 1
IsoLE 1 tAlpha 0.000012 d 10.0 E 1.0 n 0.2
BoundaryCondition 1 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 1 1 values 1 0.0 set 2
BoundaryCondition 2 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 1 3 values 1 0.0 set 3
NodalLoad 3 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 2 1 3 components 2 0. 1.0 set 4
ConstantFunction 1 f(t) 1.0
#
# partition 1
#
partest.out.1
Parallel test of explicit oofem computation
#
NlDEIDynamic nsteps 3 dumpcoef 0.0 deltaT 1.0
domain 2dTruss
#
OutputManager tstep_all dofman_all element_all
ndofman 2 nelem 1 ncrosssect 1 nmat 1 nbc 3 nic 0 nltf 1 nset 4
#
Node 2 coords 3 0. 0. 2. Shared partitions 1 0
Node 3 coords 3 0. 0. 4.
Truss2d 2 nodes 2 2 3
Set 1 elements 1 2
Set 2 nodes 2 2 3
Set 3 nodes 0
Set 4 nodes 1 3
SimpleCS 1 thick 0.1 width 10.0 material 1 set 1
IsoLE 1 tAlpha 0.000012 d 10.0 E 1.0 n 0.2
BoundaryCondition 1 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 1 1 values 1 0.0 set 2
BoundaryCondition 2 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 1 3 values 1 0.0 set 3
NodalLoad 3 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 2 1 3 components 2 0. 1.0 set 4
ConstantFunction 1 f(t) 1.0
Element-cut example¶
The example shows explicit direct integration analysis of simple structure with two DOFs. The geometry and partitioning is sketched in fig. (nodecut-ex01).
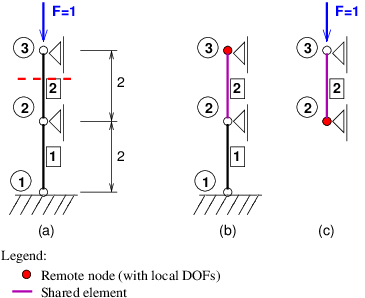
Element-cut partitioning example: (a) whole geometry, (b) partition 0, (c) partition 1.¶
#
# partition 0
#
partest2.out.0
Parallel test of explicit oofem computation
#
NlDEIDynamic nsteps 5 dumpcoef 0.0 deltaT 1.0
domain 2dTruss
#
OutputManager tstep_all dofman_all element_all
ndofman 3 nelem 2 ncrosssect 1 nmat 1 nbc 3 nic 0 nltf 1 nset 4
#
Node 1 coords 3 0. 0. 0.
Node 2 coords 3 0. 0. 2.
Node 3 coords 3 0. 0. 4. Remote partitions 1 1
Truss2d 1 nodes 2 1 2
Truss2d 2 nodes 2 2 3
Set 1 elements 2 1 2
Set 2 nodes 3 1 2 3
Set 3 nodes 1 1
Set 4 nodes 1 3
SimpleCS 1 thick 0.1 width 10.0 material 1 set 1
IsoLE 1 tAlpha 0.000012 d 10.0 E 1.0 n 0.2
BoundaryCondition 1 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 1 1 values 1 0.0 set 2
BoundaryCondition 2 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 1 3 values 1 0.0 set 3
NodalLoad 3 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 2 1 3 components 2 0. 1.0 set 4
ConstantFunction 1 f(t) 1.0
#
# partition 1
#
partest2.out.1
Parallel test of explicit oofem computation
#
NlDEIDynamic nsteps 5 dumpcoef 0.0 deltaT 1.0
domain 2dTruss
#
OutputManager tstep_all dofman_all element_all
ndofman 2 nelem 1 ncrosssect 1 nmat 1 nbc 3 nic 0 nltf 1 nset 4
#
Node 2 coords 3 0. 0. 2 Remote partitions 1 0
Node 3 coords 3 0. 0. 4
Truss2d 2 nodes 2 2 3
Set 1 elements 1 2
Set 2 nodes 2 2 3
Set 3 nodes 0
Set 4 nodes 1 3
SimpleCS 1 thick 0.1 width 10.0 material 1 set 1
IsoLE 1 tAlpha 0.000012 d 10.0 E 1.0 n 0.2
BoundaryCondition 1 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 1 1 values 1 0.0 set 2
BoundaryCondition 2 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 1 3 values 1 0.0 set 3
NodalLoad 3 loadTimeFunction 1 dofs 2 1 3 components 2 0. 1.0 set 4
ConstantFunction 1 f(t) 1.0
Figures¶

Node-cut partitioning.¶
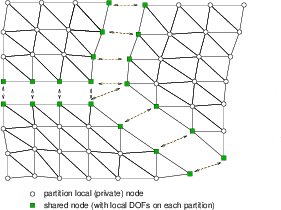
Node-cut partitioning - local constitutive mode.¶
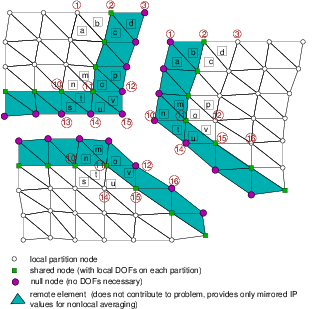
Node-cut partitioning - nonlocal constitutive mode.¶
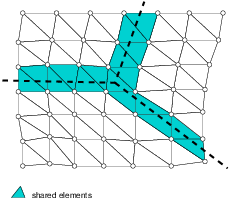
Element-cut partitioning.¶
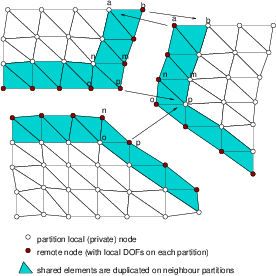
Element-cut partitioning, local constitutive mode.¶